OSSD课程干货之函数的变化
2020-05-20 环球教育
大家好,今天我们来聊一下函数的变化。
In mathematics, every function can be classified as a member of a family. Each member of a family of functions is related to the simplest, or most basic, function sharing the same characteristics. This function is called the parent function.
Certain basic functions, called parent functions, form the building blocks for families of more complicated functions. Parent functions include, but are not limited to:
在数学中,每个函数都可以归类为家庭成员。函数系列的每个成员都与共享相同特征的最简单或最基本的函数相关。此函数称为parent function
某些基本函数(称为parent function)构成了更复杂的函数族的构建基块。parent function包括但不限于:

When an object is dropped from the top of CN tower, the approximate height of the falling object above the ground is given by the function: ht=-5t2+d.
Where h(t) metres is the height of the object t seconds after it is dropped, and d metres is the height of the tower. This function is an example of a transformed parent quadratic function.

当一个物体从加拿大国家电视塔的顶部掉落时,下降物体在地面上方的大约高度由以下函数给出:ht=-5t2+d.
其中h(t)米是物体掉落后t秒的高度,d米是塔的高度。此函数是转换后的二次函数的示例。
Consider, if you add a factor d to the function, what effect does it have on the rise of the function?
这时候请思考,如果在函数后面加上一个系数d,对于函数的上升有什么样的影响?
接下来我们学习一下变换的几种形式。
Expansions, compressions, and reflections are transformations that cause functions to change shape.
Reflection is a transformation involving reflecting functions along the x-axis or y-axis.
Expansion is a transformation involving lengthening or widening a function by some real factor greater than 1. Stretches can be either horizontal or vertical.
Compression is a transformation involving making functions more compact by multiplying by some factor between 0 and 1. Compressions can be either horizontal or vertical.
扩展,压缩和反射是导致函数改变形状的变换。
翻折是一种转换,涉及沿x轴或y轴反射功能。
扩展是一种将函数加长或扩展大于1的实数的变换。拉伸可以是水平或垂直的。
压缩是通过乘以0到1之间的某个因子来使函数更紧凑的一种转换。压缩可以是水平或垂直的。
Reflection:
The graph of the function y = - f(x) is the graph of y = f(x) reflected in the x-axis. Whereas the graph of the function y = f(-x) is the graph of y = f(x) reflected in the y-axis.
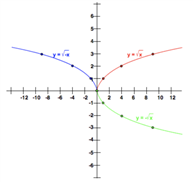
函数y=-f(x)的图形是与y=f(x)的图形关于x轴对称。而函数y=f(-x)的图形是与y=f(x)的图形关于y轴对称。
Vertical Stretching:
The graph of the y = a·f(x), a > 0 is a vertical expansion or a vertical compression of the graph y = f(x) by a factor of a.
If a > 1, then the graph is a vertical expansion by a factor(因数) of a.
If 0 < a < 1, then the graph is a vertical compression by a factor of a.
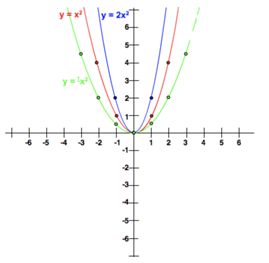
如果a > 1,那么这个图形垂直扩展了a倍,如果0 < a < 1,那么这个图形垂直压缩了a倍。
Horizontal Stretching:
The graph of the y = f(k·x),k > 0 , is a horizontal expansion or a horizontal compression of the graph y = f(x) by a factor of 1/k.
If k > 1, then the graph is a horizontal compression by a factor of 1/k.
If 0 < k < 1, then the graph is a horizontal expansion by a factor of 1/k.
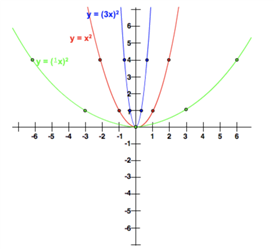
如果k> 1,那么这个图形水平压缩了k倍,如果0 < k < 1,那么这个图形水平扩展了k倍。
更多OSSD资讯可持续关注http://beijing.gedu.org

北京市海淀区环球雅思培训学校 版权所有 课程咨询热线:400-616-8800
Copyright 1997 – 2026 gedu.org. All Rights Reserved 京ICP备10036718号
全部课程、服务及教材面向18岁以上人群
市场合作申请